Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a chronic metabolic bone disease where hormonal balance defines bones’ density and quality. As a result, bones gradually become more fragile and less dense. As bone density and elasticity decreases, the risk of fractures increases, adversely affecting patients’ quality of life.
Osteoporosis is a multifactorial disease. It is mainly affected by age and lack of estrogens. However, it should not be considered as an exclusive female disease, as a growing number of osteoporosis cases, both in women and men, is due to other endocrinological diseases, drug side effects, or nutrient deficiencies (secondary osteoporosis). Increased awareness is required by the endocrinologist in order to identify and reveal the causes of secondary osteoporosis and therefore choose the most effective treatment.
IMAGE – OSTEOPOROSIS
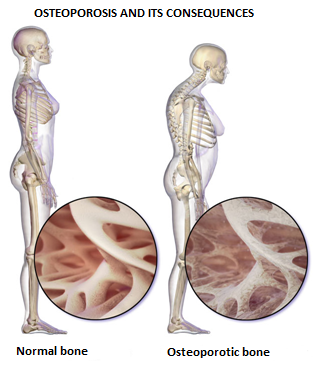
Osteoporosis is a disease without “noisy” clinical manifestations, especially at early stages, and consequently the diagnosis is often delayed. Preventive measures are necessary while the whole therapy must bepersonalized according to the medical history and the risk factors of each patient. Adequate intake of calcium and Vitamin D, nutritional attention and a variety of medication are all indicated for the treatment of osteoporosis.


